
 SOLD
SOLD
John Piper:
The Englishman's Home, 1951
Unframed (ref: 4392)
Oil on 42 panels, each panel 62 5/8 x 46 7/8 in. (159 x 119 cm.)
(187 3/4 x 609 in. (477 x 1547 cm.) overall)
Tags: John Piper oil panel architecture big pictures murals TOP 100 1.Master Designs Murals catalogue
Provenance: Harlow Art Trust
Exhibited: The Festival of Britain, 1951, The South Bank
A Tonic to the Nation, 1976, Victoria and Albert Museum
John Piper's Festival of Britain Mural, Queen Elizabeth Hall, April-May 2011
British Design 1948-2012, 2012, Victoria and Albert Museum

The Englishman's Home was painted in 1950 in the garden of the Artist's home, Fawley Bottom, Oxfordshire.
.
It
was one of the key images of the Festival of Britain and is its
largest surviving work of art. When the incoming Conservative government
attempted to cut back on the cost and scale of the Festival Hugh
Casson, the Festival's director, singled out Piper's contribution as the one mural on the South Bank we cannot afford to lose.
John
Piper and Osbert Lancaster were
the main designers of the South Bank pleasure Gardens for the festival.
The Englishman's Home adorned the exterior wall of the Homes and
Gardens Pavilion.
Sir Frederick Gibberd, masterplanner
of Harlow, selected this mural to be gifted to Harlow at the end of
the Festival of Britain.
The mural was initially entrusted to
the Harlow Development Corporation and then when the Harlow Art Trust
was formed in 1953,the Trust took charge of all four works inherited
from the Festival of Britain: Barbara Hepworth’sContrapuntal Formsand
three large murals;Boatsby Alan Sorrell,1851by Leonard
Manasseh andThe Englishman’s Homeby John Piper.The decision
to gift these four pieces to the Harlow Art Trust was approved by the
Minister of Housing and Local Government (The Rt. Hon. Hugh Dalton).
On the completion of Harlow Technical
College in the early 1960s, the mural was installed in the Assembly
Hall at the College.John Piper oversaw the installation of both this
mural and a second mural commissioned for nearby St Paul’s Church.The
installation ofThe Englishman’s Homeinvolved removing a small
section to make way for the entrance to the hall.
The mural remained at the College until
1992 when the building was firstly modified and later demolished and
the College relocated to a new site.

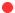
Reading from left to right the first yellow building remains unidentified, followed by the Brighton Bow fronts of Regency Square, a Victorian villa (St Martin’s Avenue, Epsom, Surrey where Piper’s Mother’s lived), 6 Station Road, (Yeovil) with Kirby Hall behind and the Royal Arms over the gateway of East Barsham Manor in Norfolk to the right, followed by the dome of Castle Howard, Yorkshire, adapted slightly for compositional effect, (also incorporating aspects of the Sheldonian Theatre in Oxford), with Owlpen Manor in Gloustershire to the right. Hillside Terraces, Brighton are depicted top right. The building to the far right remains unidentified.

IN 1951 The Peggy Guggenheim Collection at the Palazzo Venier dei Leoni in Venice opened to the public.
New buildings, for The Festival of Britain, based on London's South Bank, included The Royal Festival Hall by Leslie Martin, Peter Moro and Robert Matthew, Dome of Discovery by Ralph Tubbs.and Skylon by Philip Powell, Hidalgo Moya and Felix Samuely. Sculptures included Youth Advancing by Jacob Epstein; Reclining Figure: Festival by Henry Moore; Contrapunctal Forms and Turning Forms by Barbara Hepworth with Murals by Mary Fedden, Josef Herman and John Tunnard.
Exhibitions included Sixty Paintings for '51 at the RBA Galleries] and a show of popular and traditional art, Black Eyes & Lemonade, organised by Barbara Jones at the Whitechapel Gallery.
ARTWORKS created in 1951 included:
Henri Matisse interior decoration of Chapelle du Rosaire de Vence.
Salvador Dalí - Christ of Saint John of the Cross
Lucian Freud - Interior in Paddington
Barnett Newman – Vir Heroicus Sublimis
Pablo Picasso – Massacre in Korea
Robert Rauschenberg – White Paintings
Humphrey Ocean and Jack Vettriano were born in 1951.
Wilfrid de Glehn, (b. 1871) and Frank Newbould (b. 1887) died in 1951.



















